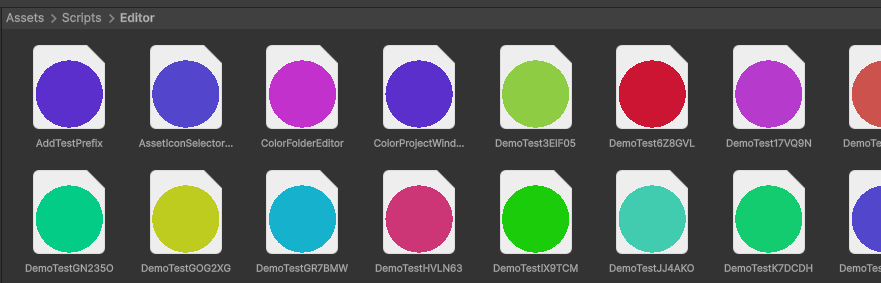
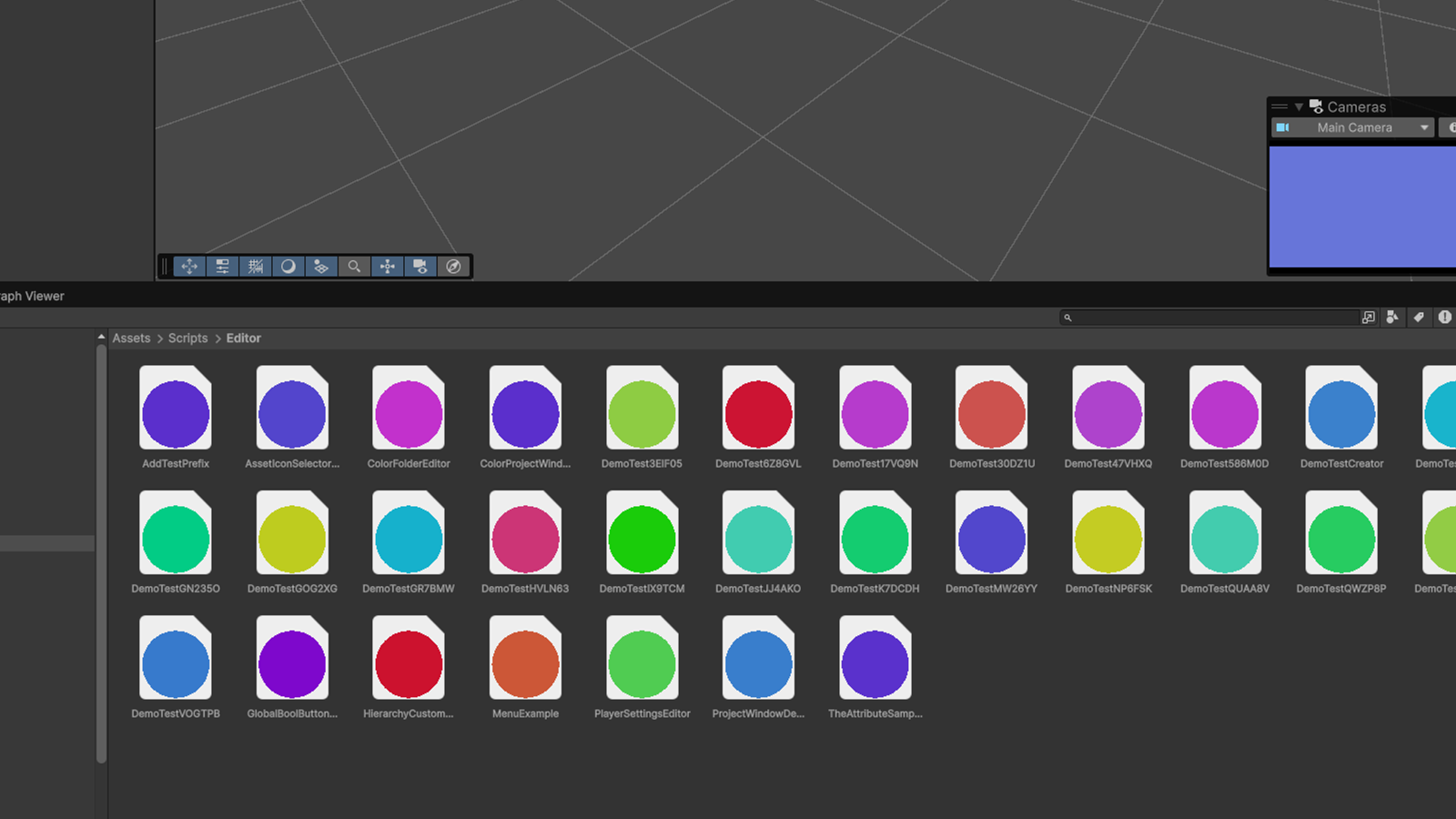
首先明确一点,编辑器开发的知识还是很多的,正确的学习方式还是从实践入手,用查工具一样的方式去学习使用。
1. Unity编辑器开发前置知识
1.1 什么是注解(Attribute)?
注解(Attribute) 是 C# 提供的一种元数据(Metadata)机制,用于在类、方法、字段、属性等上附加额外的信息。
在 Unity 编辑器开发中,注解常用于告诉 Unity 或自定义的编辑器脚本如何处理某个对象或方法。
[Serializable]
public class PlayerData
{
public int health;
public int score;
}
[SerializeField] private int health = 100;
[Range(0, 10)] public float speed = 5f;
[MenuItem("Tools/Run Custom Action")]
public static void Run() { ... }
这里的 [Serializable] 告诉 Unity 这个类可以被序列化,从而能在 Inspector 中显示。
1.2 如何给类与类的方法加注解
你可以在类、方法、字段或属性前加上方括号 [] 来声明注解。
// 给类加注解
[MyCustom("Player Class")]
public class Player
{
// 给字段加注解
[Range(0, 100)]
public int health;
// 给方法加注解
[MyCustom("Init Method")]
public void Initialize()
{
Debug.Log("Player initialized");
}
}
// 自定义一个注解类
[System.AttributeUsage(System.AttributeTargets.Class | System.AttributeTargets.Method)]
public class MyCustomAttribute : System.Attribute
{
public string Description { get; }
public MyCustomAttribute(string description)
{
Description = description;
}
}
上例中:
- MyCustomAttribute 是一个自定义注解;
[MyCustom("xxx")]表示在类或方法上附加额外说明信息。- 注意这里的命名时可以省略
Attribute,使用时也可以省略Attribute,前提是无歧义。
1.3 如何读取注解
读取注解通常通过 反射(Reflection) 实现。
using System;
using System.Reflection;
using UnityEngine;
public class AttributeReader
{
[MyCustom("Example Method")]
public void Example() { }
[ContextMenu("Test Read Attributes")]
void TestRead()
{
// 获取类型
Type type = typeof(AttributeReader);
// 遍历方法
foreach (MethodInfo method in type.GetMethods(BindingFlags.Public | BindingFlags.NonPublic | BindingFlags.Instance))
{
// 获取自定义注解
MyCustomAttribute attr = method.GetCustomAttribute<MyCustomAttribute>();
if (attr != null)
{
Debug.Log($"方法 {method.Name} 的描述为: {attr.Description}");
}
}
}
}
运行后会在 Unity 控制台输出注解内容。
这在编辑器工具中非常常见,比如扫描项目中所有打了某个标签的类并自动注册。
2. 自定义 Inspector
2.1 利用 Attribute 直接控制
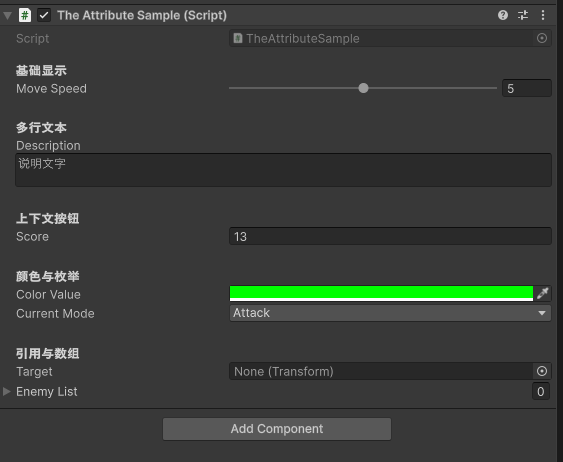
利用 Attribute 可以直接来设置 Inspector 而不用单独编写整个界面,比如下面的代码:
using UnityEngine;
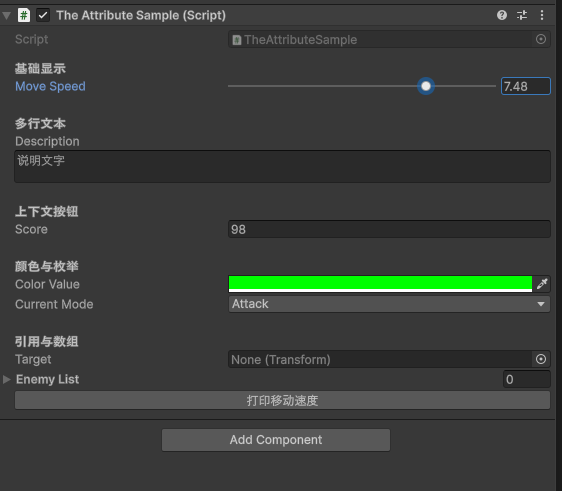
public class TheAttributeSample : MonoBehaviour
{
[Header("基础显示")]
[SerializeField, Tooltip("移动速度 (0~10)")]
[Range(0, 10)]
private float moveSpeed = 5f;
[Space]
[Header("多行文本")]
[TextArea(2, 5)]
public string description = "说明文字";
[ContextMenu("重置参数")]
private void ResetValues()
{
moveSpeed = 5f;
description = "说明文字";
Debug.Log("已重置参数");
}
[Space]
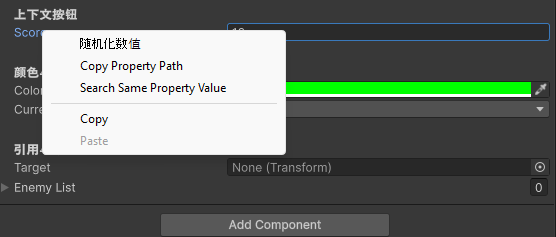
[Header("上下文按钮")]
[ContextMenuItem("随机化数值", "RandomizeValue")]
public int score = 10;
private void RandomizeValue() => score = Random.Range(0, 100);
[Space]
[Header("颜色与枚举")]
public Color colorValue = Color.green;
public Mode currentMode = Mode.Attack;
public enum Mode { Idle, Attack, Defend }
[Space]
[Header("引用与数组")]
public Transform target;
public GameObject[] enemyList;
}
在修改后:
Header添加一个标题Space是空行[Range(0, 100)]和[TextArea()]是具体的界面样式调整。[Tooltip("xxx")]是鼠标移动上去的提示。
ContextMenu 重置参数按钮控制的是组件那个地方。
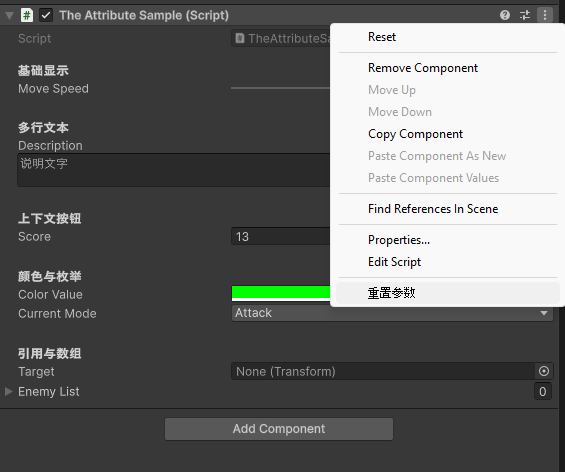
ContextMenuItem 是在属性的右键菜单中。
2.2 CustomEditor / 自定义界面的方法
前面的 Attribute 与逻辑代码还是贴在一起的,很方便但是自定义程度还不够。
我们可以专门为一个 Component 来编写它的 Inspector,下面就来介绍这种方法。
首先要确保我们的代码的 .cs 文件需要放在任意的名为 Editor 的文件夹下面,然后使用 CustomEditor 来实现自定义绘制。
using System;
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEditor;
[CustomEditor(typeof(TheAttributeSample))] // 关联脚本类型
public class TheAttributeSampleEditor : Editor
{
SerializedProperty moveSpeed;
private void OnEnable()
{
moveSpeed = serializedObject.FindProperty("moveSpeed");
}
public override void OnInspectorGUI()
{
// 1. 更新序列化对象
serializedObject.Update();
// 2. 绘制默认属性
DrawDefaultInspector();
// 3. 自定义按钮
if (GUILayout.Button("打印移动速度"))
{
Debug.Log("MoveSpeed = " + moveSpeed.floatValue);
}
// 4. 应用修改
serializedObject.ApplyModifiedProperties();
}
}
[CustomEditor(typeof(TheAttributeSample))]表示关联的类是TheAttributeSampleOnInspectorGUI会在显示和输入更改时调用。OnInspectorGUI是override意味着可以通过base.OnInspectorGUI()来表示默认界面。
这里还有个稍微复杂点的用法,就是可以有参数:
public CustomEditor(System.Type inspectedType, bool editorForChildClasses)
public bool isFallback { get; set; }
// 使用下面这行可替换全局 MonoBehaviour 的 Inspector
[CustomEditor(typeof(MonoBehaviour), true, isFallback = true)]
这样可以直接替换掉全局的 MonoBehaviour,但是 isFallback = true 保证了只有没任何其他可用项的时候才会使用当前的这个。
2.3 生命周期
在运行时(Play Mode)我们有:
Awake → OnEnable → Start → Update → OnDisable → OnDestroy
在编辑器扩展(Editor Mode)中也有类似的体系,只不过发生在编辑器层面:
OnEnable → OnInspectorGUI / OnSceneGUI (重复执行) → OnDisable
这些回调运行在 UnityEditor 命名空间下;Unity 会在编辑器状态变动(比如脚本重编译、选中物体、打开 Inspector 等)时自动触发。
Editor 生命周期完整流程(按时间顺序):
| 阶段 | 回调方法 | 调用时机 | 常见用途 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 初始化阶段 | OnEnable() | 当 Inspector 打开 / 选中物体 / 脚本重编译时 | 缓存 SerializedProperty、注册事件、初始化资源 |
| 激活阶段 | OnInspectorGUI() | 每次 Inspector 重绘时调用(非常频繁) | 绘制 UI、检测用户输入、修改数据 |
| 场景绘制阶段 | OnSceneGUI() | 当对象在 Scene 视图中被选中或 Scene 视图重绘时 | 绘制 Gizmo、Handles、交互操作 |
| 预览阶段 | HasPreviewGUI() / OnPreviewGUI() | 在 Inspector 底部绘制预览(模型、音频等) | 自定义资源预览窗口 |
| 更新阶段 | OnInspectorUpdate() | 编辑器定期刷新(大约 10 FPS) | 定时刷新状态、检测异步任务 |
| 销毁阶段 | OnDisable() | 当 Inspector 被关闭、切换选中对象或 Domain Reload 时 | 注销事件、释放内存、清理引用 |
2.4 Editor.serializedObject
在 Editor 脚本中,serializedObject 是一个特殊的对象,它是对你正在编辑的脚本(即 target)的一个 序列化包装(封装层)。
如果你在 Editor 里直接写:
((MyScript)target).speed = 5;
它不支持:
- Undo
- Prefab 标记覆盖
- 多选对象 target 时无法统一修改
Unity 的序列化系统解决了这些问题,所以提供了 serializedObject。
serializedObject= 当前目标对象(target)的序列化版本SerializedProperty= 该对象中的一个字段的序列化包装
比如:
SerializedProperty moveSpeed;
void OnEnable()
{
moveSpeed = serializedObject.FindProperty("moveSpeed");
}
public override void OnInspectorGUI()
{
serializedObject.Update();
EditorGUILayout.PropertyField(speed);
serializedObject.ApplyModifiedProperties();
}
上面代码可以这么理解:Update 是把 target 的数据同步到 serializedObject,EditorGUILayout.PropertyField 是自动根据类型显示在操作界面,修改的时候会同步回传。而 ApplyModifiedProperties 是把 serializedObject 的修改,传递回 target。
2.5 GUILayout / IMGUI
GUILayout 属于 IMGUI(Immediate Mode GUI)系统,它是最基础的 GUI 绘制类,能在:
MonoBehaviour.OnGUI()(游戏运行时)Editor.OnInspectorGUI()(编辑器自定义 Inspector)EditorWindow.OnGUI()(自定义编辑器窗口)
中使用。
在 Editor 里使用时,一般我们这样写:
public override void OnInspectorGUI()
{
GUILayout.Label("标题");
}
简记:Label / Text / Toggle / Slider / Button / Layout
一个综合的例子:
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEditor;
[CustomEditor(typeof(TheAttributeSample))]
public class TheAttributeSampleEditor : Editor
{
private bool toggleValue = true;
private float sliderValue = 5f;
private string inputText = "初始文本";
private string multiLine = "多行文本\n支持换行";
private Vector2 scrollPos;
public override void OnInspectorGUI()
{
// 标题
GUILayout.Label("👋 自定义 Inspector - GUILayout 控件演示", EditorStyles.boldLabel);
GUILayout.Space(10);
// 输入框
GUILayout.Label("单行文本输入:");
inputText = GUILayout.TextField(inputText);
GUILayout.Space(5);
// 多行输入框
GUILayout.Label("多行文本输入:");
multiLine = GUILayout.TextArea(multiLine, GUILayout.Height(60));
GUILayout.Space(5);
// 开关
toggleValue = GUILayout.Toggle(toggleValue, "启用某个功能");
GUILayout.Space(5);
// 滑条
GUILayout.Label($"移动速度: {sliderValue:F2}");
sliderValue = GUILayout.HorizontalSlider(sliderValue, 0, 10);
GUILayout.Space(10);
// 按钮
if (GUILayout.Button("打印当前状态"))
{
Debug.Log($"输入: {inputText}, 开关: {toggleValue}, 速度: {sliderValue}");
}
GUILayout.Space(10);
GUILayout.Box("", GUILayout.ExpandWidth(true), GUILayout.Height(2)); // 分隔线
// 滚动区域
GUILayout.Label("滚动区域示例:");
scrollPos = GUILayout.BeginScrollView(scrollPos, GUILayout.Height(100));
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++)
{
GUILayout.Label("项目 " + i);
}
GUILayout.EndScrollView();
GUILayout.Space(10);
GUILayout.Label("布局控制:");
GUILayout.BeginHorizontal();
if (GUILayout.Button("左按钮")) Debug.Log("左");
if (GUILayout.Button("右按钮")) Debug.Log("右");
GUILayout.EndHorizontal();
GUILayout.Space(5);
GUILayout.Label("示例结束 🎯");
}
}
样式:
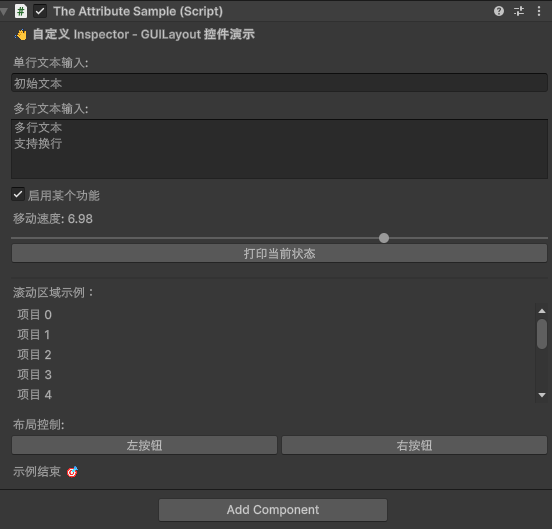
2.6 EditorGUILayout
EditorGUILayout 是 Unity 编辑器脚本里的一个工具类,它可以帮你在 Inspector 或 自定义窗口里显示各种控件,比如按钮、滑条、颜色选择器等。
自动支持 Undo、Prefab 覆盖、多对象编辑。
和 GUILayout 的区别是,它支持多对象,写起来更简洁,样式统一。
常用控件:
| 控件 | 用途 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| LabelField | 显示文本 | EditorGUILayout.LabelField("标题") |
| TextField | 输入单行文字 | EditorGUILayout.TextField("名字", name) |
| TextArea | 多行文字 | EditorGUILayout.TextArea(description) |
| Toggle | 开关 | EditorGUILayout.Toggle("是否启用", isOn) |
| Slider | 滑条 | EditorGUILayout.Slider("速度", speed, 0, 10) |
| IntField | 整数输入 | EditorGUILayout.IntField("生命", hp) |
| FloatField | 浮点输入 | EditorGUILayout.FloatField("速度", speed) |
| Vector3Field | 三维向量 | EditorGUILayout.Vector3Field("位置", pos) |
| ColorField | 颜色选择 | EditorGUILayout.ColorField("颜色", color) |
| ObjectField | 拖拽对象 | EditorGUILayout.ObjectField("目标", obj, typeof(GameObject), true) |
| EnumPopup | 下拉选择枚举 | EditorGUILayout.EnumPopup("类型", playerClass) |
| Foldout | 折叠面板 | fold = EditorGUILayout.Foldout(fold, "高级") |
| PropertyField | 自动绘制 SerializedProperty | EditorGUILayout.PropertyField(serializedProp) |
一个案例:
using UnityEngine;
public class PlayerSettings : MonoBehaviour
{
[SerializeField, Range(0, 10)]
private float moveSpeed = 5f;
[SerializeField]
private string playerName = "Hero";
[SerializeField]
private Color playerColor = Color.cyan;
[SerializeField]
private bool isGodMode = false;
}
Editor 部分:
using UnityEditor;
using UnityEngine;
[CustomEditor(typeof(PlayerSettings))]
public class PlayerSettingsEditor : Editor
{
// 定义 SerializedProperty 对象
SerializedProperty moveSpeed;
SerializedProperty playerName;
SerializedProperty playerColor;
SerializedProperty isGodMode;
// 初始化:在编辑器加载时绑定字段
void OnEnable()
{
moveSpeed = serializedObject.FindProperty("moveSpeed");
playerName = serializedObject.FindProperty("playerName");
playerColor = serializedObject.FindProperty("playerColor");
isGodMode = serializedObject.FindProperty("isGodMode");
}
// 自定义 Inspector 界面
public override void OnInspectorGUI()
{
// 同步目标对象的最新数据
serializedObject.Update();
GUILayout.Label("🎮 Player Settings", EditorStyles.boldLabel);
EditorGUILayout.Space();
// 绘制属性字段(自动支持撤销 / Prefab)
EditorGUILayout.PropertyField(playerName, new GUIContent("Player Name"));
EditorGUILayout.PropertyField(moveSpeed, new GUIContent("Move Speed"));
EditorGUILayout.PropertyField(playerColor, new GUIContent("Player Color"));
EditorGUILayout.PropertyField(isGodMode, new GUIContent("God Mode"));
EditorGUILayout.Space(10);
// 添加一个自定义按钮
if (GUILayout.Button("打印玩家信息"))
{
var player = (PlayerSettings)target;
Debug.Log($"👤 {playerName.stringValue} - 速度: {moveSpeed.floatValue}, 无敌: {isGodMode.boolValue}");
}
// 提交修改回目标对象
serializedObject.ApplyModifiedProperties();
}
}
效果:
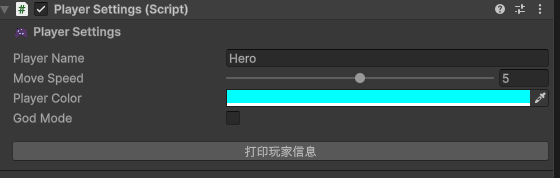
完全可以理解为是一个抽象了一个中间层的 IMGUI,避免手动绑定一些写法。如果复杂点写,还可以实现下面的效果:
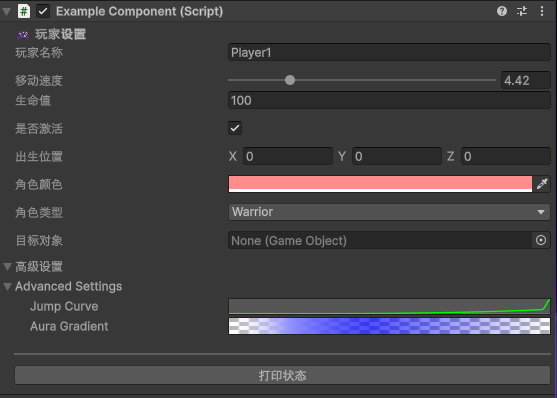
2.6.1 展开折叠的例子
这个例子虽然简单,但是由于太过常用,这里专门写一下。
展开折叠的例子:
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEditor;
[CustomEditor(typeof(PlayerSettings))]
public class PlayerSettingsEditor : Editor
{
// SerializedProperty 对象
SerializedProperty moveSpeed;
SerializedProperty playerName;
SerializedProperty playerColor;
SerializedProperty isGodMode;
// 折叠状态变量
bool showBasicSettings = true;
bool showAdvancedSettings = false;
void OnEnable()
{
moveSpeed = serializedObject.FindProperty("moveSpeed");
playerName = serializedObject.FindProperty("playerName");
playerColor = serializedObject.FindProperty("playerColor");
isGodMode = serializedObject.FindProperty("isGodMode");
}
public override void OnInspectorGUI()
{
serializedObject.Update();
// 折叠面板:基础设置
showBasicSettings = EditorGUILayout.Foldout(showBasicSettings, "基础设置");
if (showBasicSettings)
{
EditorGUILayout.PropertyField(playerName);
EditorGUILayout.PropertyField(moveSpeed);
}
EditorGUILayout.Space();
// 折叠面板:高级设置
showAdvancedSettings = EditorGUILayout.Foldout(showAdvancedSettings, "高级设置");
if (showAdvancedSettings)
{
EditorGUILayout.PropertyField(playerColor);
EditorGUILayout.PropertyField(isGodMode);
}
EditorGUILayout.Space();
// 打印按钮
if (GUILayout.Button("打印玩家信息"))
{
Debug.Log($"玩家 {playerName.stringValue}, 速度 {moveSpeed.floatValue}, " +
$"颜色 {playerColor.colorValue}, 无敌: {isGodMode.boolValue}");
}
serializedObject.ApplyModifiedProperties();
}
}
效果实现:
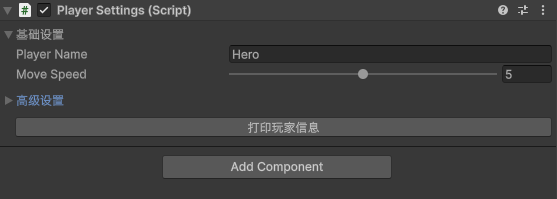
2.7 Handles / OnSceneGUI
OnSceneGUI 是 Unity 自定义编辑器里的一个回调函数,允许你在 Scene 视图中绘制和交互,每次 Scene 视图刷新时自动调用。
Handles 是 Unity 提供的一组 Scene 视图可视化控件和绘图工具:
| 方法 | 用途 |
|---|---|
Handles.PositionHandle | 可拖拽控制位置 |
Handles.RotationHandle | 可旋转控制 |
Handles.ScaleHandle | 可缩放控制 |
Handles.Label | 显示文本标签 |
Handles.SphereHandleCap | 绘制球体 |
Handles.DrawLine | 绘制线条 |
Handles.DrawWireCube | 绘制空心方块 |
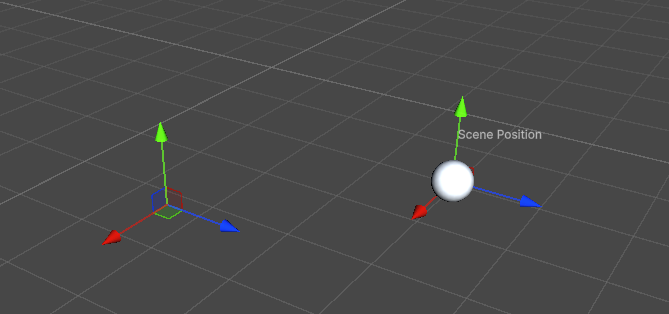
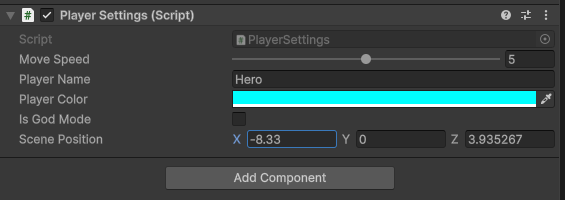
我们直接上使用方式。首先给 PlayerSettings 增加一个三维坐标,后面会用 Handles 来可视化操作这个三维坐标。
public class PlayerSettings : MonoBehaviour
{
// ...
//
public Vector3 scenePosition = Vector3.zero;
}
然后在 OnSceneGUI 中通过 Handles 来实现操作 scenePosition 的可视化修改。
using UnityEditor;
using UnityEditor.TerrainTools;
using UnityEngine;
[CustomEditor(typeof(PlayerSettings))]
public class PlayerSettingsEditor : Editor
{
private void OnSceneGUI()
{
PlayerSettings player = (PlayerSettings)target;
// 开始监测修改
EditorGUI.BeginChangeCheck();
// 拖拽 PositionHandle 控制 scenePosition
Vector3 newPos = Handles.PositionHandle(player.scenePosition, Quaternion.identity);
if (EditorGUI.EndChangeCheck())
{
Undo.RecordObject(player, "Move Scene Position"); // 支持 Undo
player.scenePosition = newPos; // 更新位置
EditorUtility.SetDirty(player); // 标记对象已修改
}
// 绘制一个球体标记
Handles.color = Color.aliceBlue;
Handles.SphereHandleCap(0, player.scenePosition, Quaternion.identity, 0.5f, EventType.Repaint);
// 绘制名字标签
Handles.Label(player.scenePosition + Vector3.up * 0.6f, "Scene Position");
}
}
效果:
- 注意,这里必须要选择这个物体,才会在 Scene 中进行绘制,和下面要介绍的 Gizmo 是有区别的。
这个坐标还是可以在 Inspector 中直接编辑的,不影响这一点。
2.8 Gizmos / OnDrawGizmos
Handles 只能在 Scene 中进行绘制,而且必须要选中。
Gizmos 可以同时在 Scene 和 Game 中绘制并显示,准确来说这个知识是不算是 Editor 开发里面的,这里只是对比讲解下 Handles。
| 方法 | 用途 |
|---|---|
Gizmos.DrawLine(start, end) | 绘制直线 |
Gizmos.DrawRay(origin, direction) | 绘制射线 |
Gizmos.DrawSphere(center, radius) | 绘制球体 |
Gizmos.DrawCube(center, size) | 绘制方块 |
Gizmos.DrawWireCube(center, size) | 绘制空心方块 |
Gizmos.color | 设置颜色 |
Gizmos.DrawIcon(position, iconName, allowScaling) | 绘制图标 |
还是回到 PlayerSettings,我们的目标是用 Gizmos 显示它:
using UnityEngine;
public class PlayerSettings : MonoBehaviour
{
[SerializeField, Range(0, 10)]
private float moveSpeed = 5f;
[SerializeField]
private string playerName = "Hero";
[SerializeField]
private Color playerColor = Color.cyan;
[SerializeField]
private bool isGodMode = false;
public Vector3 scenePosition = Vector3.zero;
private void OnDrawGizmos()
{
Gizmos.color = playerColor;
// 绘制球体
Gizmos.DrawSphere(scenePosition, 0.5f);
// 绘制一条向上的线
Gizmos.DrawLine(scenePosition, scenePosition + Vector3.up);
// 绘制名字标签(Scene 中仅显示)
UnityEditor.Handles.Label(scenePosition + Vector3.up * 0.6f, playerName);
}
}
可以在 Game 中也看到,注意要把右上角的 Gizmos 给启用才能看到:
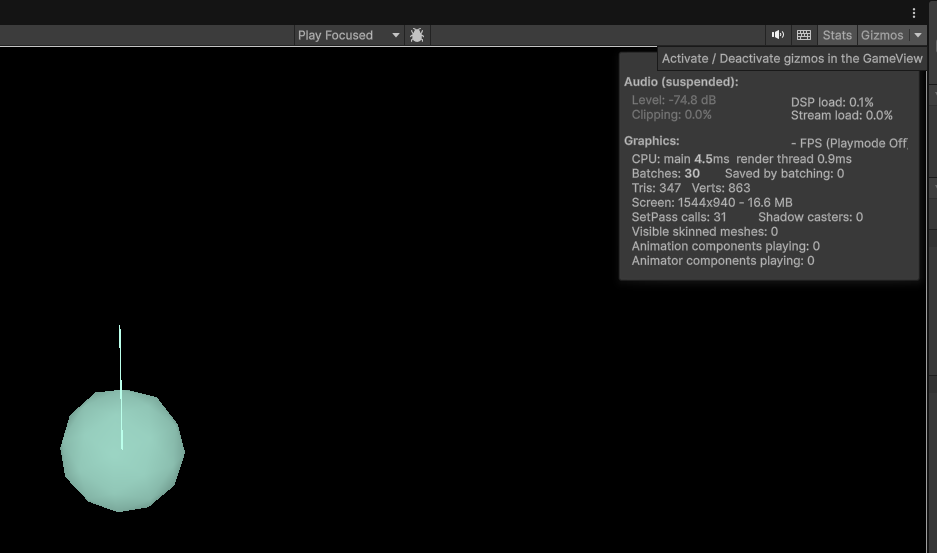
3. 工具类
3.1 EditorUtility
EditorUtility 是 Unity 编辑器提供的 实用工具类,用来完成一些通用编辑器操作,比如弹窗、标记对象修改、保存等。
下面的 SetDirty 经常用到。
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
EditorUtility.SetDirty(Object obj) | 标记对象已修改,确保编辑器保存更改 |
EditorUtility.DisplayDialog(title, message, ok, cancel) | 弹出对话框 |
EditorUtility.DisplayProgressBar(title, info, progress) | 显示进度条 |
EditorUtility.ClearProgressBar() | 关闭进度条 |
EditorUtility.FocusProjectWindow() | 聚焦 Project 窗口 |
EditorUtility.CopySerialized(Object src, Object dst) | 复制对象数据 |
using UnityEditor;
using UnityEngine;
public class EditorUtilityExample
{
[MenuItem("Tools/Mark Dirty Example")]
static void MarkDirtyExample()
{
GameObject go = Selection.activeGameObject;
if (go != null)
{
Undo.RecordObject(go, "Modify GameObject");
go.transform.position = Vector3.one;
EditorUtility.SetDirty(go); // 标记修改
Debug.Log("GameObject position changed and marked dirty.");
}
}
}
3.2 AssetDatabase
AssetDatabase 是 Unity 的资源管理接口,用于操作项目中的资源(创建、删除、导入、查找等)。
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
AssetDatabase.CreateAsset(Object asset, string path) | 创建资源文件 |
AssetDatabase.DeleteAsset(string path) | 删除资源文件 |
AssetDatabase.MoveAsset(string oldPath, string newPath) | 移动/重命名资源 |
AssetDatabase.LoadAssetAtPath<T>(string path) | 加载资源 |
AssetDatabase.Refresh() | 刷新资源数据库 |
AssetDatabase.GetAssetPath(Object obj) | 获取资源路径 |
using UnityEditor;
using UnityEngine;
public class AssetDatabaseExample
{
[MenuItem("Tools/Create Material")]
static void CreateMaterial()
{
Material mat = new Material(Shader.Find("Standard"));
AssetDatabase.CreateAsset(mat, "Assets/NewMaterial.mat");
AssetDatabase.SaveAssets();
AssetDatabase.Refresh();
Debug.Log("Material created in Assets folder.");
}
}
3.3 Selection
Selection 用来 获取或设置编辑器当前选中的对象,常用在编辑器工具中操作用户选择的对象。
| 属性 / 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
Selection.activeObject | 当前选中的对象(单选) |
Selection.activeGameObject | 当前选中的 GameObject(单选) |
Selection.objects | 当前选中的所有对象(多选) |
Selection.gameObjects | 当前选中的所有 GameObject(多选) |
Selection.activeTransform | 当前选中对象的 Transform |
Selection.activeInstanceID | 当前选中对象的实例 ID |
using UnityEditor;
using UnityEngine;
public class SelectionExample
{
[MenuItem("Tools/Print Selected Objects")]
static void PrintSelectedObjects()
{
foreach (var obj in Selection.objects)
{
Debug.Log("Selected object: " + obj.name);
}
}
}
3.4 EditorWindow.OnGUI
每当 Unity 需要绘制界面(Inspector、EditorWindow、Game GUI等)时,就会自动调用 OnGUI(),让你用代码即时画出 UI 控件。
| 上下文 | 触发方式 | 用途 |
|---|---|---|
| MonoBehaviour.OnGUI() | 游戏运行时调用 | 绘制简单 HUD、调试 GUI |
| EditorWindow.OnGUI() | 编辑器窗口 | 绘制自定义工具窗口 |
| Editor.OnInspectorGUI() | Inspector 面板 | 自定义组件的 Inspector |
| EditorApplication.projectWindowItemOnGUI | Project 窗口绘制 | 绘制资源背景/图标 |
| EditorApplication.projectWindowItemInstanceOnGUI | Project 窗口绘制 | 绘制资源背景/图标,可以处理子资产 |
| EditorApplication.hierarchyWindowItemOnGUI | Hierarchy 绘制 | 修改 GameObject 显示效果 |
利用 EditorWindow 的 GUI 创建一个窗口:
using UnityEditor;
using UnityEngine;
public class SimpleWindow : EditorWindow
{
[MenuItem("Window/Simple GUI")]
public static void ShowWindow()
{
GetWindow<SimpleWindow>("Simple GUI");
}
void OnGUI()
{
GUILayout.Label("Hello Unity IMGUI!", EditorStyles.boldLabel);
if (GUILayout.Button("Click Me"))
{
Debug.Log("Button clicked!");
}
}
}
实现效果:
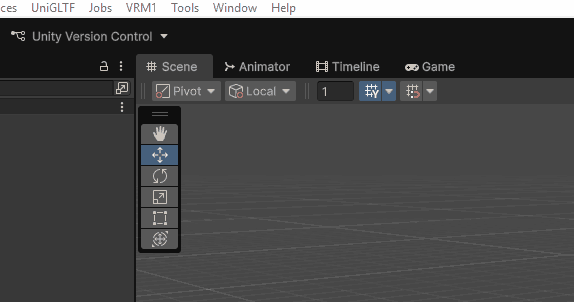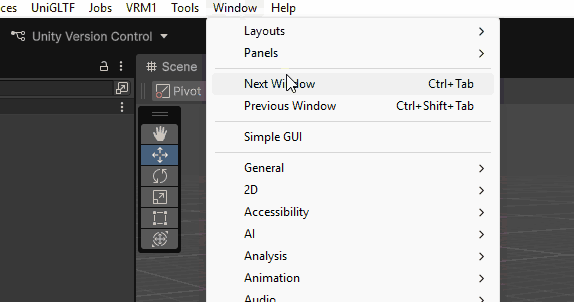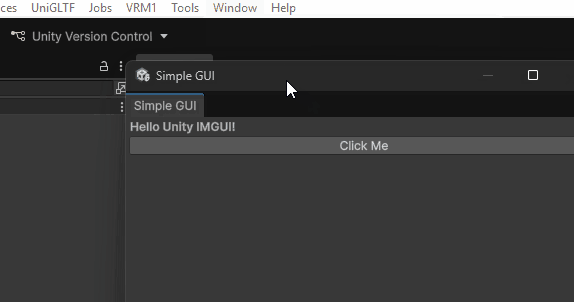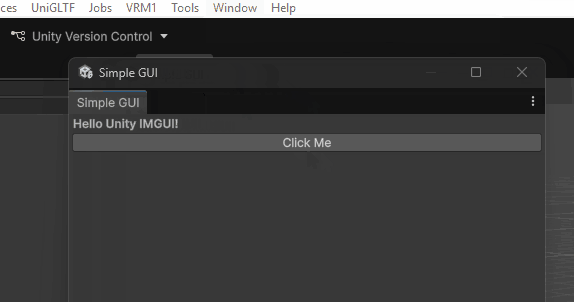
3.5 projectWindowItemOnGUI
projectWindowItemOnGUI 是 Unity Editor 提供的一个 静态回调事件,用于在 Project 窗口的每个资源条目上绘制自定义 GUI。
注意这里要注销一下上次注册的,这是一个比较好的习惯。
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEditor;
[InitializeOnLoad]
public static class ProjectWindowDecorator
{
static ProjectWindowDecorator()
{
EditorApplication.projectWindowItemOnGUI -= OnProjectWindowItemGUI;
EditorApplication.projectWindowItemOnGUI += OnProjectWindowItemGUI;
}
private static void OnProjectWindowItemGUI(string guid, Rect rect)
{
string path = AssetDatabase.GUIDToAssetPath(guid);
// 只对 png 文件生效
if (path.EndsWith(".png"))
{
// 在资源右上角画一个红色小圆点
Rect dotRect = new Rect(rect.xMax - 10, rect.y + 2, 8, 8);
EditorGUI.DrawRect(dotRect, Color.red);
}
}
}
效果:
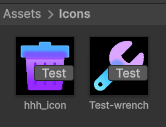
还可以实现给每个文件上加一个按钮的功能:
3.6 EditorPrefs
EditorPrefs 是 Unity 编辑器专用的一个类,用来在本地保存编辑器级别的配置数据(类似于“编辑器偏好设置”)。
它的功能类似于 PlayerPrefs(游戏运行时存储),但用于编辑器工具或插件的设置。
它不会随着 “项目移动” 而迁移,也就是仅仅是你本机电脑保存的。
通常不用这个,如果有需要的话,应该是写成一个可以保存的 JSON 之类的,跟着项目可以同步。
using UnityEditor;
using UnityEngine;
public class EditorPrefsExample
{
[MenuItem("Tools/EditorPrefs 示例")]
public static void Example()
{
// 保存数据
EditorPrefs.SetString("MyTool_LastFilePath", "D:/MyProject/Config.txt");
EditorPrefs.SetInt("MyTool_UseDarkTheme", 1);
EditorPrefs.SetBool("MyTool_ShowTips", true);
EditorPrefs.SetFloat("MyTool_Volume", 0.8f);
// 读取数据
string path = EditorPrefs.GetString("MyTool_LastFilePath", "未设置");
bool showTips = EditorPrefs.GetBool("MyTool_ShowTips", false);
float volume = EditorPrefs.GetFloat("MyTool_Volume", 1.0f);
Debug.Log($"路径: {path}, 是否显示提示: {showTips}, 音量: {volume}");
// 删除数据
EditorPrefs.DeleteKey("MyTool_LastFilePath");
// 检查是否存在
if (EditorPrefs.HasKey("MyTool_UseDarkTheme"))
Debug.Log("暗色主题设置存在");
}
}
3.7 MonoBehaviour.OnGUI
严格来说这个也不算 Editor 开发,但是这个很适合制作一些测试用只在 Editor 运行游戏时使用的按钮,比如下面的代码:
using UnityEngine;
public class TestMonoOnGUI : MonoBehaviour
{
#if UNITY_EDITOR
void OnGUI()
{
if (GUI.Button(new Rect(10, 10, 100, 30), "Click Me"))
{
Debug.Log("按钮被点击了!");
}
}
#endif
}
运行后能出现一个按钮,并且这个按钮因为宏限制在了只能用于编辑器运行的情况,不会影响正式游戏。
4 MenuItem
4.1 顶部菜单栏
MenuItem 是 Unity 提供的一个 编辑器注解,用于在菜单栏或右键菜单中添加自定义功能。
如果路径是不以 Assets/ 或 GameObject/ 开头,Unity 会把它放在顶部菜单栏。
using UnityEditor;
using UnityEngine;
public class MenuExample
{
[MenuItem("Tools/Print Message")]
public static void PrintMessage()
{
Debug.Log("Hello from Tools menu!");
}
[MenuItem("Tools/Print Message", true)] // 验证函数(用于启用/禁用菜单项)
public static bool ValidatePrintMessage()
{
return Application.isPlaying == false; // 仅在非运行状态可用
}
}
在上方出现:
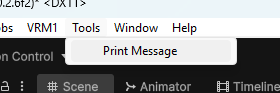
说明:
- [MenuItem(“Tools/Print Message”)] 会在 Unity 菜单栏的 Tools 下添加一个 “Print Message” 菜单项。
[MenuItem("路径", true)]带有 true 参数的表示同名方法是验证函数,用来控制菜单是否可用,如果返回 false 那么会是灰色 不可点击状态 。- 方法必须是 static。
第三项是 优先级 ,控制菜单在同级菜单中的排序,数字越小越靠上。
[MenuItem("Tools/Print Debug", false, 10)]
4.2 右键菜单栏
Assets/ 开头可以在 Project 窗口中右键出现,而 GameObject/ 开头可以在 Hierarchy 里面出现。
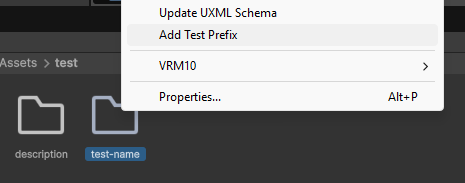
这里实现下面一个功能:
- 在
Project窗口右键文件夹时显示菜单,多选时也能生效,并对文件夹名字加上test-前缀(如果没有的话)
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEditor;
public class AddTestPrefix
{
// 右键菜单显示在 Project 窗口文件夹上
[MenuItem("Assets/Add Test Prefix", true)]
private static bool ValidateAddTestPrefix()
{
// 只允许选中文件夹
foreach (var obj in Selection.objects)
{
string path = AssetDatabase.GetAssetPath(obj);
if (!AssetDatabase.IsValidFolder(path))
return false;
}
return Selection.objects.Length > 0;
}
[MenuItem("Assets/Add Test Prefix")]
private static void AddPrefix()
{
foreach (var obj in Selection.objects)
{
string path = AssetDatabase.GetAssetPath(obj);
if (!AssetDatabase.IsValidFolder(path))
continue;
string folderName = System.IO.Path.GetFileName(path);
if (!folderName.StartsWith("test"))
{
string newFolderName = "test-" + folderName;
string parentPath = System.IO.Path.GetDirectoryName(path).Replace("\\", "/");
string newPath = parentPath + "/" + newFolderName;
AssetDatabase.RenameAsset(path, newFolderName);
Debug.Log($"Renamed folder: {folderName} -> {newFolderName}");
}
}
AssetDatabase.SaveAssets();
AssetDatabase.Refresh();
}
}
演示:
5. 风格美化
5.1 True/False 变开关按钮
如果我们期望实现一个开关按钮,而不是勾选,怎么做呢?
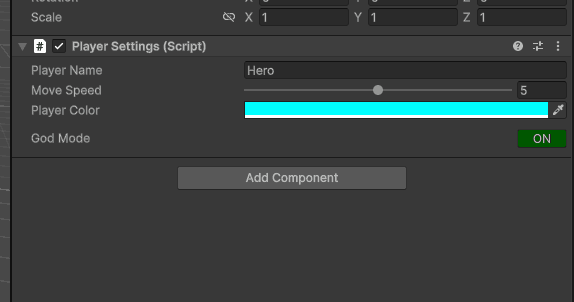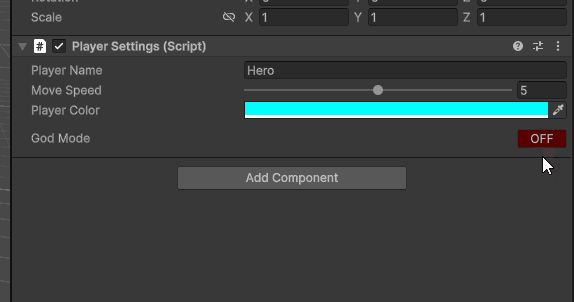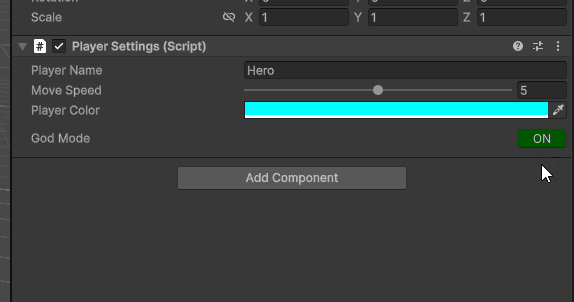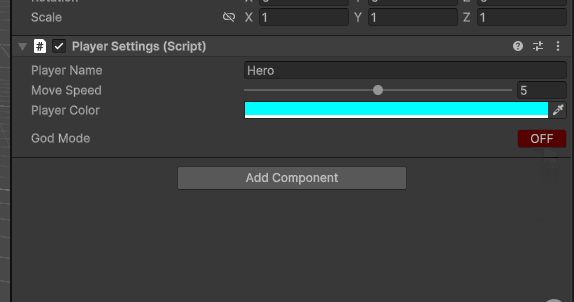
包括水平布局,更改按钮的背景颜色,
代码:
using UnityEditor;
using UnityEngine;
[CustomEditor(typeof(PlayerSettings))]
public class PlayerSettingsEditor : Editor
{
private SerializedProperty moveSpeed;
private SerializedProperty playerName;
private SerializedProperty playerColor;
private SerializedProperty isGodMode;
private void OnEnable()
{
moveSpeed = serializedObject.FindProperty("moveSpeed");
playerName = serializedObject.FindProperty("playerName");
playerColor = serializedObject.FindProperty("playerColor");
isGodMode = serializedObject.FindProperty("isGodMode");
}
public override void OnInspectorGUI()
{
serializedObject.Update();
// 基础属性
EditorGUILayout.PropertyField(playerName);
EditorGUILayout.PropertyField(moveSpeed);
EditorGUILayout.PropertyField(playerColor);
EditorGUILayout.Space();
// ----------------- 按钮靠右 -----------------
EditorGUILayout.BeginHorizontal();
// 左侧标签
EditorGUILayout.LabelField("God Mode");
// 中间占位,使按钮靠右
GUILayout.FlexibleSpace();
// 右侧按钮
GUI.backgroundColor = isGodMode.boolValue ? Color.green : Color.red;
if (GUILayout.Button(isGodMode.boolValue ? "ON" : "OFF", GUILayout.Width(50)))
{
isGodMode.boolValue = !isGodMode.boolValue;
EditorUtility.SetDirty(target);
}
EditorGUILayout.EndHorizontal();
serializedObject.ApplyModifiedProperties();
}
}
5.2 全局样式替换
也许你会想说,那么能不能把所有地方的 bool 都替换了?
Editor 确实给了我们这种接口:
代码:
using UnityEditor;
using UnityEngine;
// ✅ 作用于所有 bool 字段
[CustomPropertyDrawer(typeof(bool))]
public class GlobalBoolButtonDrawer : PropertyDrawer
{
public override void OnGUI(Rect position, SerializedProperty property, GUIContent label)
{
// 只处理 bool
if (property.propertyType != SerializedPropertyType.Boolean)
{
EditorGUI.PropertyField(position, property, label, true);
return;
}
// ---------------- 绘制布局 ----------------
var labelRect = new Rect(position.x, position.y, EditorGUIUtility.labelWidth, position.height);
var buttonRect = new Rect(position.x + EditorGUIUtility.labelWidth + 5, position.y, 50, position.height);
// 标签
EditorGUI.LabelField(labelRect, label);
// 按钮颜色
var oldColor = GUI.backgroundColor;
GUI.backgroundColor = property.boolValue ? Color.green : Color.red;
// 按钮样式
if (GUI.Button(buttonRect, property.boolValue ? "ON" : "OFF"))
{
property.boolValue = !property.boolValue;
}
GUI.backgroundColor = oldColor;
}
public override float GetPropertyHeight(SerializedProperty property, GUIContent label)
{
return EditorGUIUtility.singleLineHeight + EditorGUIUtility.standardVerticalSpacing;
}
}
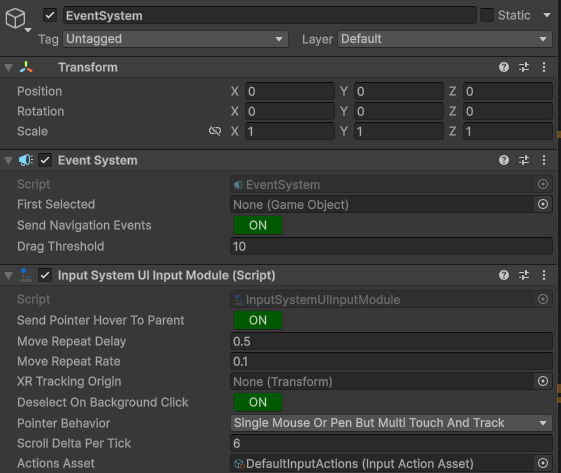
回到界面中,可以看到,连 Event System 这种地方,也直接改了:
5.3 Hierarchy 美化
利用 EditorApplication.hierarchyWindowItemOnGUI 可以实现绘制 Hierarchy 的时候进行一些自定义操作。
例如实现下面的变色功能:
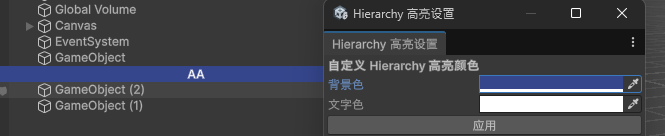
配合持久化实现改变色彩功能。
代码:
using UnityEditor;
using UnityEngine;
[InitializeOnLoad]
public class HierarchyCustomDrawer
{
private const string PrefixName = ":";
// EditorPrefs Key
private const string BackgroundColorKey = "HierarchyBackgroundColor";
private const string TextColorKey = "HierarchyTextColor";
// 默认颜色
public static Color BackgroundColor = Color.magenta;
public static Color TextColor = Color.white;
static HierarchyCustomDrawer()
{
LoadColors();
EditorApplication.hierarchyWindowItemOnGUI -= OnHierarchyGUI;
EditorApplication.hierarchyWindowItemOnGUI += OnHierarchyGUI;
}
private static void LoadColors()
{
// 读取背景色
string bgStr = EditorPrefs.GetString(BackgroundColorKey, "FF00FF"); // 默认紫色
if (!ColorUtility.TryParseHtmlString("#" + bgStr, out BackgroundColor))
{
BackgroundColor = Color.magenta;
}
// 读取文字色
string textStr = EditorPrefs.GetString(TextColorKey, "FFFFFF"); // 默认白色
if (!ColorUtility.TryParseHtmlString("#" + textStr, out TextColor))
{
TextColor = Color.white;
}
}
static void OnHierarchyGUI(int instanceID, Rect selectionRect)
{
GameObject obj = EditorUtility.InstanceIDToObject(instanceID) as GameObject;
if (obj == null) return;
if (obj.name.StartsWith(PrefixName))
{
// 绘制背景
Rect backgroundRect = new Rect(0, selectionRect.y, Screen.width, selectionRect.height);
EditorGUI.DrawRect(backgroundRect, BackgroundColor);
// 绘制文字
string name = obj.name.Substring(PrefixName.Length).Trim();
GUIStyle style = new GUIStyle(EditorStyles.label)
{
alignment = TextAnchor.MiddleCenter,
fontStyle = FontStyle.Bold,
wordWrap = true,
normal = { textColor = TextColor }
};
EditorGUI.LabelField(backgroundRect, name, style);
}
}
// 菜单打开窗口
[MenuItem("Tools/Hierarchy 高亮设置")]
public static void OpenColorSettings()
{
HierarchyColorWindow.ShowWindow();
}
}
public class HierarchyColorWindow : EditorWindow
{
private Color backgroundColor;
private Color textColor;
public static void ShowWindow()
{
var window = GetWindow<HierarchyColorWindow>("Hierarchy 高亮设置");
window.minSize = new Vector2(250, 100);
window.LoadCurrentColors();
}
private void LoadCurrentColors()
{
backgroundColor = HierarchyCustomDrawer.BackgroundColor;
textColor = HierarchyCustomDrawer.TextColor;
}
private void OnGUI()
{
GUILayout.Label("自定义 Hierarchy 高亮颜色", EditorStyles.boldLabel);
backgroundColor = EditorGUILayout.ColorField("背景色", backgroundColor);
textColor = EditorGUILayout.ColorField("文字色", textColor);
if (GUILayout.Button("应用"))
{
// 保存到 EditorPrefs(字符串)
EditorPrefs.SetString("HierarchyBackgroundColor", ColorUtility.ToHtmlStringRGBA(backgroundColor));
EditorPrefs.SetString("HierarchyTextColor", ColorUtility.ToHtmlStringRGBA(textColor));
// 更新静态变量
HierarchyCustomDrawer.BackgroundColor = backgroundColor;
HierarchyCustomDrawer.TextColor = textColor;
// 刷新 Hierarchy
EditorApplication.RepaintHierarchyWindow();
}
}
}
5.4 设置组件图标
使用 EditorGUIUtility.SetIconForObject 来给一个资产设置图标,但是这个是对 C# 是不行的,重新打开就没了。
正确的方法是用 MonoImporter.SetIcon 和 monoImporter.SaveAndReimport 来持久化,这样同时组件图标也改了。
![]()
组件中样式:
![]()
代码:
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEditor;
public class AssetIconSelectorWindow : EditorWindow
{
private Texture2D selectedIcon;
[MenuItem("Tools/Set Asset Icon Window")]
public static void ShowWindow()
{
GetWindow<AssetIconSelectorWindow>("Set Asset Icon");
}
private void OnGUI()
{
GUILayout.Label("批量设置资产图标", EditorStyles.boldLabel);
// 获取当前选中的所有资产
Object[] selectedAssets = Selection.objects;
// 显示选中的资产列表
if (selectedAssets.Length == 0)
{
EditorGUILayout.LabelField("未选择资产");
}
else
{
EditorGUILayout.LabelField($"选中 {selectedAssets.Length} 个资产:");
foreach (Object asset in selectedAssets)
{
EditorGUILayout.LabelField(" - " + asset.name);
}
}
// 选择图标
selectedIcon = (Texture2D)EditorGUILayout.ObjectField("图标", selectedIcon, typeof(Texture2D), false);
GUILayout.Space(10);
if (GUILayout.Button("应用图标到选中资产"))
{
ApplyIcon(selectedAssets);
}
}
private void ApplyIcon(Object[] assets)
{
if (assets == null || assets.Length == 0)
{
EditorUtility.DisplayDialog("错误", "请先在 Project 面板选择一个或多个资产", "确定");
return;
}
if (selectedIcon == null)
{
EditorUtility.DisplayDialog("错误", "请选择一个图标", "确定");
return;
}
int appliedCount = 0;
foreach (Object asset in assets)
{
string path = AssetDatabase.GetAssetPath(asset);
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(path))
continue;
// 持久化设置
var importer = AssetImporter.GetAtPath(path) as MonoImporter;
if (importer != null)
{
importer.SetIcon(selectedIcon);
importer.SaveAndReimport();
appliedCount++;
}
}
EditorUtility.DisplayDialog("完成", $"图标已应用到 {appliedCount} 个资产", "确定");
}
}
6. 自定义类型
一个极其常见的需求:导入一个自定义的文件,例如 “.vrm” 等。这些是如何处理的呢?
这里以 “.hhh” 为例,它是一个纯文本文件,只有 2 行,第一行表示 name,第二行表示 description 。
6.1 ScriptableObject
导入的文件实际上上面的套了一个 ScriptableObject 才能显示,这里创建 2 个 ScriptableObject,将分别作为 .hhh 的主对象,和非主对象。
using UnityEngine;
[CreateAssetMenu(fileName = "NewHHHFile", menuName = "Custom/HHH File")]
public class HHHFile : ScriptableObject
{
public string nameLine;
public string descriptionLine;
}
public class HHHName : ScriptableObject
{
public string nameLine;
}
6.2 AssetImporter 解析
然后在文件导入时,通过写 ScriptedImporter 可以实现解析过程。
创建了 HHHFile 实例并读取 name 和 description,然后将这个实例设置为主对象,同时设置了图标。
同时创建了一个 HHHName 实例,并设置为非主对象。
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEditor;
using UnityEditor.AssetImporters;
using System.IO;
[ScriptedImporter(1, "hhh")]
public class HHHImporter : ScriptedImporter
{
public override void OnImportAsset(AssetImportContext ctx)
{
// 读取文件内容
string[] lines = File.ReadAllLines(ctx.assetPath);
// 1️⃣ 主对象 HHHFile
HHHFile mainAsset = ScriptableObject.CreateInstance<HHHFile>();
mainAsset.nameLine = lines.Length > 0 ? lines[0] : "";
mainAsset.descriptionLine = lines.Length > 1 ? lines[1] : "";
ctx.AddObjectToAsset("HHHFile", mainAsset);
ctx.SetMainObject(mainAsset);
// 设置主对象图标
Texture2D mainIcon = AssetDatabase.LoadAssetAtPath<Texture2D>("Assets/Icons/hhh_icon.png");
if (mainIcon != null)
{
EditorGUIUtility.SetIconForObject(mainAsset, mainIcon);
}
// 2️⃣ 非主对象 HHHName
HHHName subAsset = ScriptableObject.CreateInstance<HHHName>();
subAsset.nameLine = mainAsset.nameLine;
ctx.AddObjectToAsset(subAsset.nameLine, subAsset);
// 设置非主对象图标
Texture2D subIcon = AssetDatabase.LoadAssetAtPath<Texture2D>("Assets/Icons/wrench.png");
if (subIcon != null)
{
EditorGUIUtility.SetIconForObject(subAsset, subIcon);
}
}
}
导入后效果:
能够在右侧查看 Inspector:
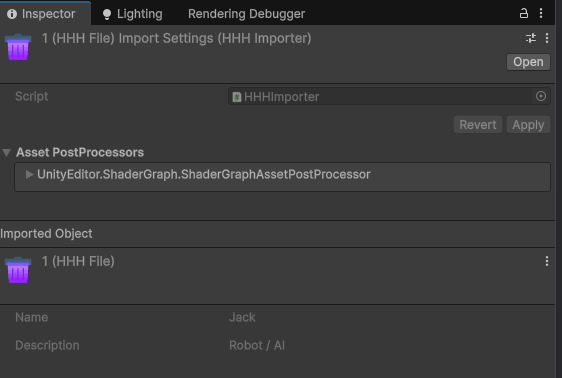
这里添加了一个 Inspector CustomEditor,和前面介绍的美化方式是一个意思,作用只是告诉你这个 HHHFile 一样是可以自定义 Inspector 的。
using UnityEditor;
[CustomEditor(typeof(HHHFile))]
public class HHHFileInspector : Editor
{
public override void OnInspectorGUI()
{
HHHFile hhh = (HHHFile)target;
EditorGUILayout.LabelField("Name", hhh.nameLine);
EditorGUILayout.Space();
EditorGUILayout.LabelField("Description", hhh.descriptionLine);
}
}
6.3 AssetPostprocessor
任何资产的变动,即导入、删除、移动,都可以触发 OnPostprocessAllAssets。通过对这个函数的编写,能够实现一些后处理,比如自动设置导入的图片为 sprite 等。
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEditor;
using System.IO;
public class HHHFilePostprocessor : AssetPostprocessor
{
static void OnPostprocessAllAssets(
string[] importedAssets,
string[] deletedAssets,
string[] movedAssets,
string[] movedFromAssetPaths)
{
foreach (string path in importedAssets)
{
// 只处理 .hhh 文件
if (Path.GetExtension(path) == ".hhh")
{
// 读取文件内容
string[] lines = File.ReadAllLines(path);
string nameLine = lines.Length > 0 ? lines[0] : "";
string descLine = lines.Length > 1 ? lines[1] : "";
// 打印日志
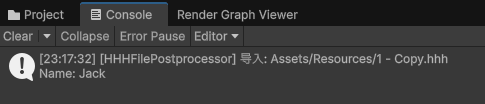
Debug.Log($"[HHHFilePostprocessor] 导入: {path}\nName: {nameLine}\nDescription: {descLine}");
}
}
}
}
导入的时候就会打印这行信息:
7. 随机颜色
Just For Fun
给文件一个随机的颜色,根据文件名 Hash 唯一确定。
using System;
using UnityEditor;
using UnityEngine;
[InitializeOnLoad]
public static class ColorProjectWindowDecorator
{
static ColorProjectWindowDecorator()
{
EditorApplication.projectWindowItemOnGUI -= OnProjectWindowItemGUI;
EditorApplication.projectWindowItemOnGUI += OnProjectWindowItemGUI;
}
private static void OnProjectWindowItemGUI(string guid, Rect rect)
{
string path = AssetDatabase.GUIDToAssetPath(guid);
// 只针对 .cs 文件
if (!path.EndsWith(".cs", StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase))
return;
// 提取文件名
string fileName = System.IO.Path.GetFileNameWithoutExtension(path);
// 计算一个确定性的哈希值
int hash = fileName.GetHashCode();
// 将哈希映射到颜色(HSV -> RGB)
float hue = Mathf.Abs(hash % 360) / 360f; // 色相
float saturation = 0.6f + (Mathf.Abs(hash) % 40) / 100f; // 0.6~1.0
float value = 0.8f; // 亮度固定
Color color = Color.HSVToRGB(hue, saturation, value);
float size = Math.Min(rect.width, rect.height) * 0.7f;
Rect dotRect = new Rect(
rect.x + rect.width / 2f - size / 2f,
rect.y + rect.height / 2f - size / 2f,
size,
size
);
DrawCircle(dotRect, color);
}
private static void DrawCircle(Rect rect, Color color)
{
// 用 Handles 绘制圆形(比方形更柔和)
Handles.BeginGUI();
Color oldColor = Handles.color;
Handles.color = color;
Handles.DrawSolidDisc(rect.center, Vector3.forward, rect.width / 2);
Handles.color = oldColor;
Handles.EndGUI();
}
}